publications
publications by categories in reversed chronological order. generated by jekyll-scholar.
Note: \(\dagger\) indicates corresponding author, \(*\) indicates equal contribution.
2025
- KBS
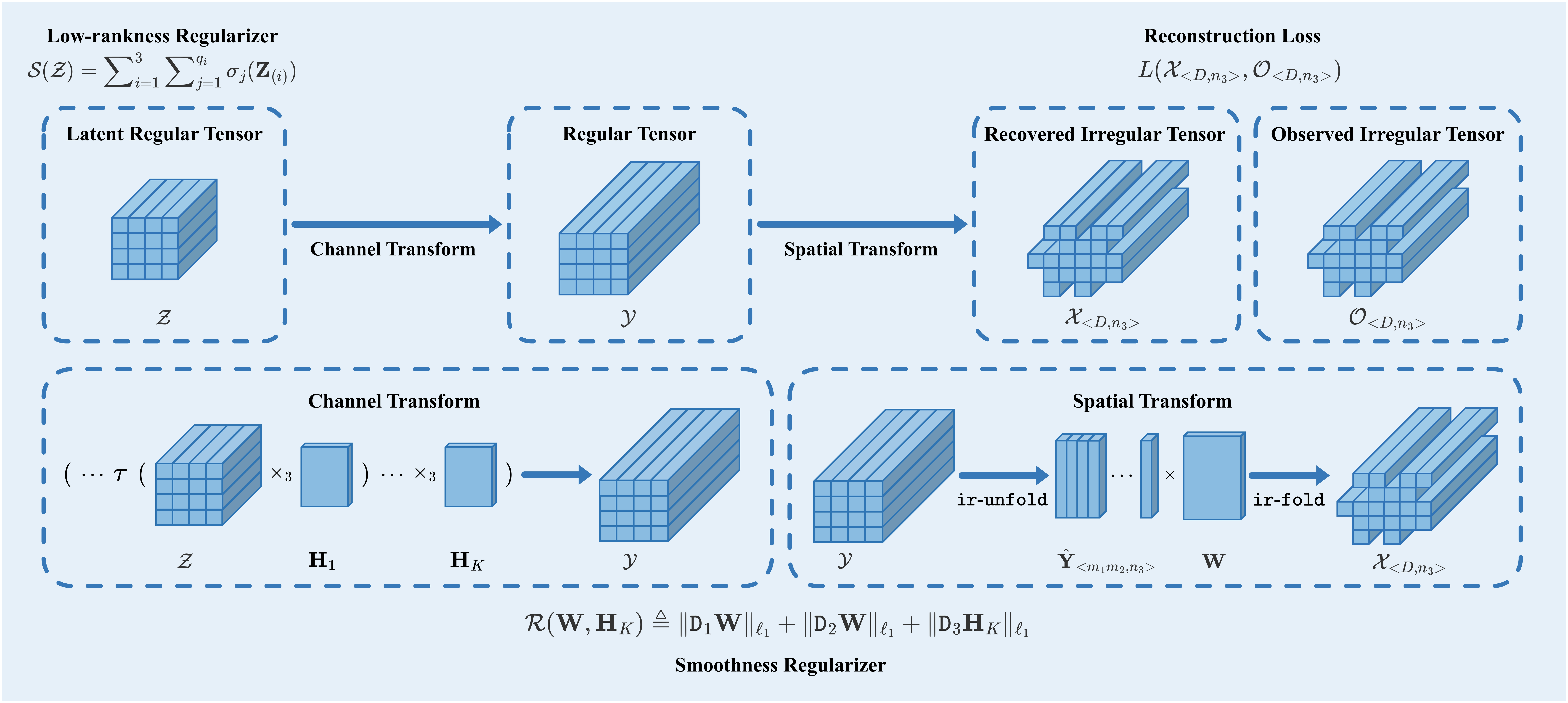 IRTF: A New Tensor Factorization for Irregular Multidimensional Data RecoveryKnowledge-Based Systems, 2025
IRTF: A New Tensor Factorization for Irregular Multidimensional Data RecoveryKnowledge-Based Systems, 2025Tensor factorizations, although serving as paramount tools for exploiting prior knowledge of multidimensional data, are unsuitable for emerging irregular multidimensional data with the arbitrary shape spatial domain (i.e., spatial-irregular tensor), such as superpixels and spatial transcriptomics. Developing new tensor factorizations suitable for spatial-irregular tensors poses a compelling challenge. To meet this challenge, we introduce a novel Irregular Tensor Factorization (IRTF), which can fully capture the intrinsic spatial and channel information behind the spatial-irregular tensor. Concretely, a spatial-irregular tensor can be decomposed into the product of an intrinsic regular tensor, learnable channel transform matrices, and a learnable spatial transform matrix. Accompanying IRTF, we suggest the Total Variation on Channel and Spatial Transforms (TV-CST) to exploit the local information of spatial-irregular tensors, which is hardly excavated by traditional total variation methods. Combining the proposed IRTF and TV-CST, we built a spatial-irregular tensor recovery model. Extensive experiments on real-world spatial-irregular tensors demonstrate the promising performance of our IRTF and its significant advantages on downstream tasks.
@article{kbs, author = {Xie, Jin-Yu and Zhang, Hao and Zhao, Xi-Le and Luo, Yi-Si}, journal = {Knowledge-Based Systems}, title = {{IRTF}: A New Tensor Factorization for Irregular Multidimensional Data Recovery}, keywords = {Tensor factorization, Irregular multidimensional data, Total variation}, year = {2025}, doi = {10.1016/j.knosys.2025.114372}, }
2024
- ACM TKDD
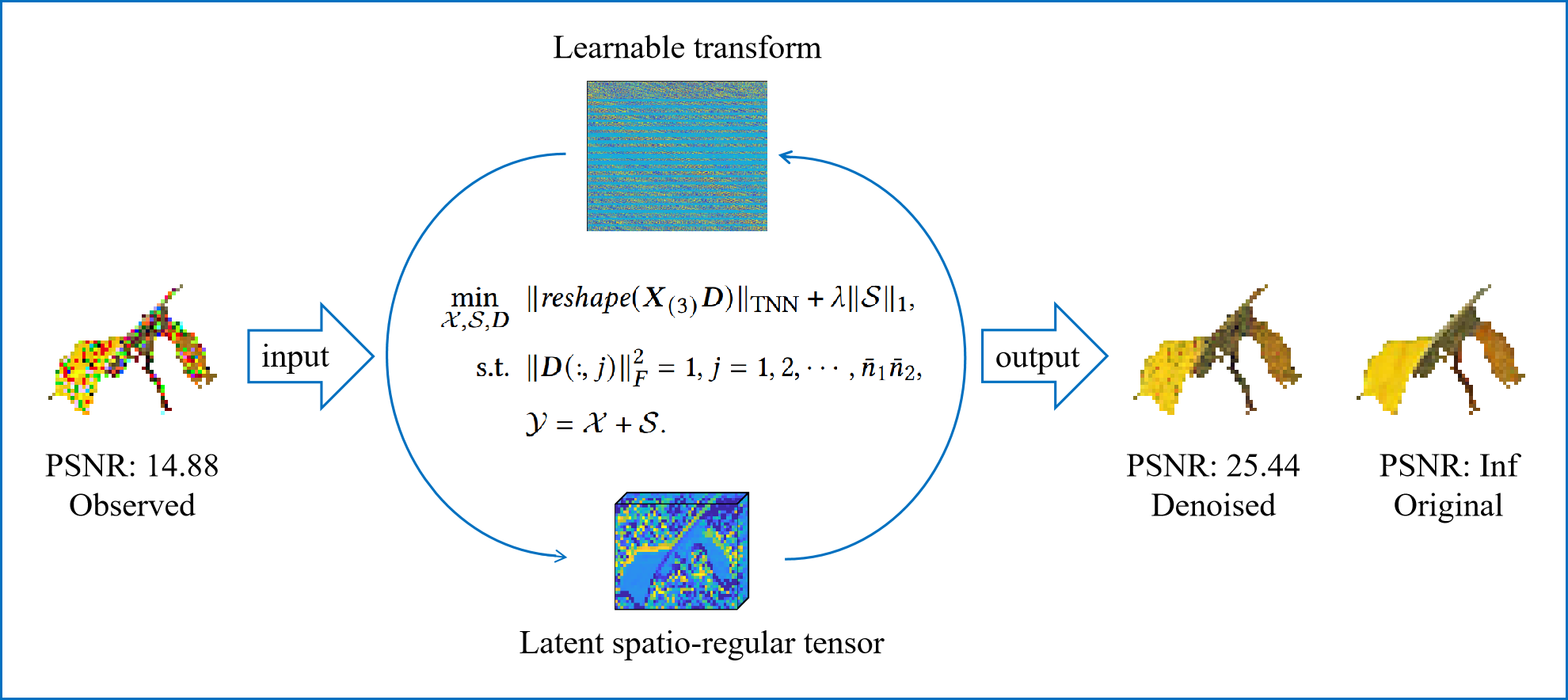 Learnable Transform-Assisted Tensor Decomposition for Spatio-Irregular Multidimensional Data RecoveryHao Zhang, Ting-Zhu Huang, Xi-Le Zhao, Shu-Qin Zhang, Jin-Yu Xie, Tai-Xiang Jiang, and Michael K. NgACM Transactions on Knowledge Discovery from Data, 2024
Learnable Transform-Assisted Tensor Decomposition for Spatio-Irregular Multidimensional Data RecoveryHao Zhang, Ting-Zhu Huang, Xi-Le Zhao, Shu-Qin Zhang, Jin-Yu Xie, Tai-Xiang Jiang, and Michael K. NgACM Transactions on Knowledge Discovery from Data, 2024Tensor decompositions have been successfully applied to multidimensional data recovery. However, classical tensor decompositions are not suitable for emerging spatio-irregular multidimensional data (i.e., spatio-irregular tensor), whose spatial domain is non-rectangular, e.g., spatial transcriptomics data from bioinformatics and semantic units from computer vision. By using preprocessing (e.g., zero-padding or element-wise 0-1 weighting), the spatio-irregular tensor can be converted to a spatio-regular tensor and then classical tensor decompositions can be applied, but this strategy inevitably introduces bias information, leading to artifacts. How to design a tensor-based method suitable for emerging spatio-irregular tensors is an imperative challenge. To address this challenge, we propose a learnable transform-assisted tensor singular value decomposition (LTA-TSVD) for spatio-irregular tensor recovery, which allows us to leverage the intrinsic structure behind the spatio-irregular tensor. Specifically, we design a learnable transform to project the original spatio-irregular tensor into its latent spatio-regular tensor, and then the latent low-rank structure is captured by classical TSVD on the resulting regular tensor. Empowered by LTA-TSVD, we develop spatio-irregular low-rank tensor completion (SIR-LRTC) and spatio-irregular tensor robust principal component analysis (SIR-TRPCA) models for the spatio-irregular tensor imputation and denoising respectively, and we design corresponding solving algorithms with theoretical convergence. Extensive experiments including the spatial transcriptomics data imputation and hyperspectral image denoising show SIR-LRTC and SIR-TRPCA are superior performance to competing approaches and benefit downstream applications.
@article{LTA-TSVD, author = {Zhang, Hao and Huang, Ting-Zhu and Zhao, Xi-Le and Zhang, Shu-Qin and Xie, Jin-Yu and Jiang, Tai-Xiang and Ng, Michael K.}, journal = {ACM Transactions on Knowledge Discovery from Data}, title = {Learnable Transform-Assisted Tensor Decomposition for Spatio-Irregular Multidimensional Data Recovery}, year = {2024}, doi = {10.1145/3701235}, } - IEEE IGARSS
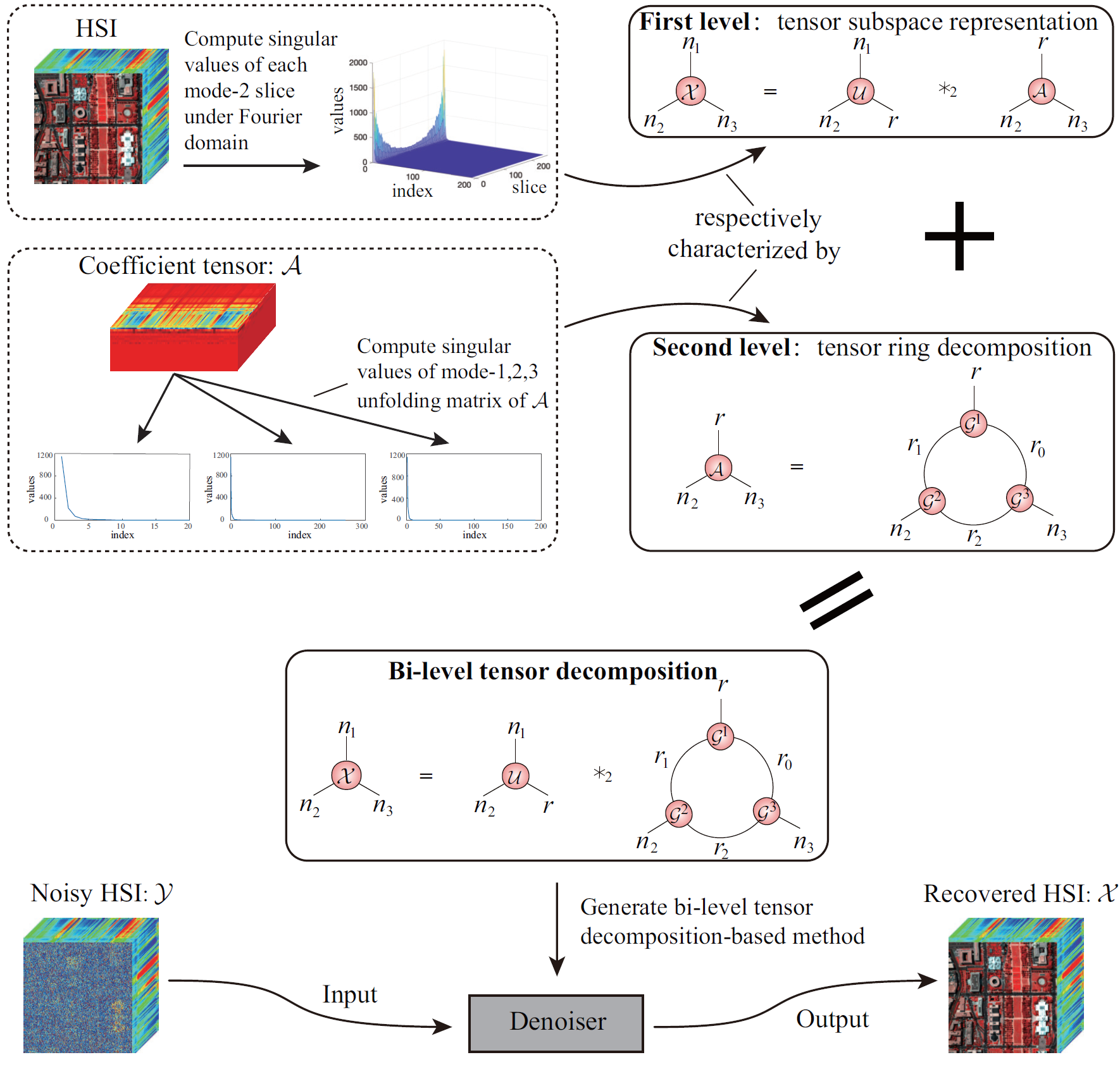 Bi-Level Tensor Decomposition for Hyperspectral Image RestorationIn IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, 2024
Bi-Level Tensor Decomposition for Hyperspectral Image RestorationIn IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, 2024This paper proposes a bi-level tensor decomposition (BLTD), properly exploiting the characterization advantages of tensor subspace representation (TSR) and tensor ring decomposition (TRD). More specifically, the first level is related to the decomposition of a third-order tensor into its TSR using the tensor-tensor product (t-product), and the second level performs TRD on the coefficient tensor obtained by TSR. Leveraging the proposed BLTD, we design a bi-level tensor nuclear norm (BLTNN)-based model for hyperspectral images (HSIs) denoising. To solve the model, we develop an efficient alternating direction method of multipliers (ADMM)-based algorithm. Experimental results demonstrate the superior performance of our method compared to existing methods.
@inproceedings{BLTD, author = {Liu, Yun-Yang and Zhao, Xi-Le and Xie, Jin-Yu and Xu, Zhi and Vivone, Gemine}, title = {Bi-Level Tensor Decomposition for Hyperspectral Image Restoration}, year = {2024}, doi = {10.1109/IGARSS53475.2024.10640494}, booktitle = {IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium}, }
2023
- IEEE GRSL
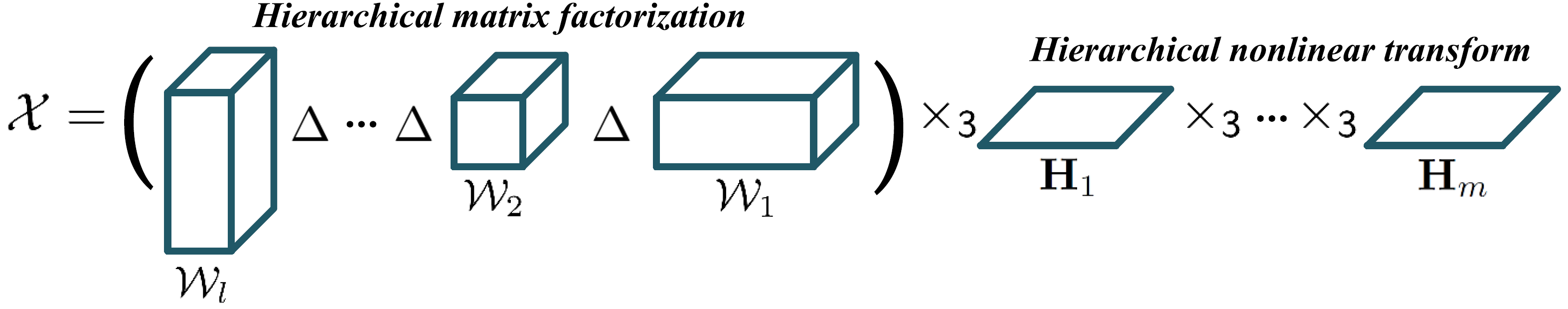 H2TF for Hyperspectral Image Denoising: Where Hierarchical Nonlinear Transform Meets Hierarchical Matrix FactorizationIEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2023
H2TF for Hyperspectral Image Denoising: Where Hierarchical Nonlinear Transform Meets Hierarchical Matrix FactorizationIEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2023Recently, tensor singular value decomposition(t-SVD) has emerged as a promising tool for hyperspectral image (HSI) processing. In the t-SVD, there are two key building blocks: 1) the low-rank enhanced transform and 2) the accompanying low-rank characterization of transformed frontal slices. Previous t-SVD methods mainly focus on the developments of 1), while neglecting the other important aspect, i.e., the exact characterization of transformed frontal slices. In this letter, we exploit the potentiality in both building blocks by leveraging the hierarchical nonlinear transform (HNT) and the hierarchical matrix factorization (HMF) to establish a new tensor factorization (termed as H2TF). Compared with shallow counter partners, e.g., low-rank matrix factorization (MF) or its convex surrogates, H2TF can better capture complex structures of transformed frontal slices due to its hierarchical modeling abilities. We then suggest the H2TF-based HSI denoising model and develop an alternating direction method of multipliers-based algorithm to address the resultant model. Extensive experiments validate the superiority of our method over state-of-the-art (SOTA) HSI denoising methods.
@article{h2tf, author = {Xie, Jin-Yu and Li, Jia-Yi and Luo, Yi-Si and Zhao, Xi-Le and Wang, Jian-Li}, journal = {IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters}, title = {{H2TF} for Hyperspectral Image Denoising: Where Hierarchical Nonlinear Transform Meets Hierarchical Matrix Factorization}, year = {2023}, volume = {20}, doi = {10.1109/LGRS.2023.3294933}, }